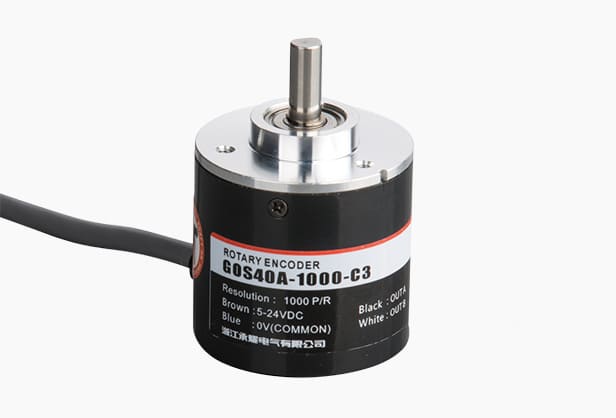
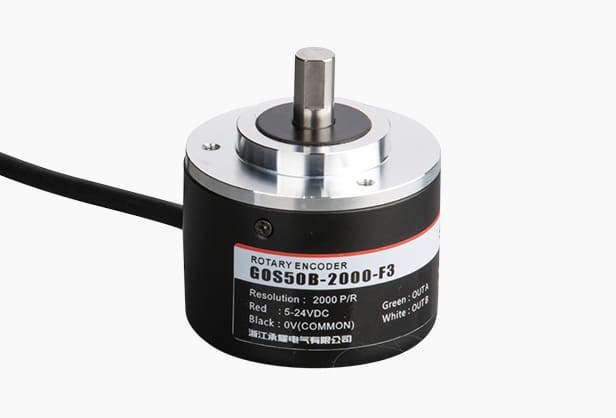
Automation systems demand precision to ensure efficiency and reliability. Incremental rotary encoders play a vital role in achieving this by providing accurate feedback on position, speed, and direction. These devices have become essential in modern industries due to their ability to meet the growing need for precision control.
- The market for incremental rotary encoders has grown significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the rise of Industry 4.0.
- High-resolution capabilities, such as up to 4,096 pulses per revolution, ensure precise position sensing in industrial applications.
- Integration with IoT and AI technologies further highlights their importance in delivering real-time feedback for smart manufacturing.
Their compact design and durability make them suitable for harsh environments, ensuring consistent performance even under challenging conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Incremental rotary encoders give exact details about position, speed, and direction.
- They can measure up to 4,096 pulses per turn for accuracy.
- These encoders are strong and work well in tough conditions.
- They connect with IoT and AI to help monitor and predict issues.
- Picking the right encoder depends on your needs, like resolution and environment.
Understanding Incremental Rotary Encoders
Definition and Core Functionality
An incremental rotary encoder is a device that converts the angular motion or position of a rotating shaft into digital or analog signals. These signals provide feedback on position, speed, and direction, making them essential for precision control in automation systems. You’ll often find two main types of incremental encoders: rotary and linear. Rotary encoders use a circular disc with slots to generate signals, while linear encoders work along a straight path.
Industry standards define incremental rotary encoders with specific technical specifications. Here’s a quick overview:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Diameter | φ 16 to 36 mm |
| Length | 11 mm to 12 mm |
| Resolution | 32 ppr to 360 ppr |
| Max. Channels | 3 |
| Operating Temperature | -40~125 ℃ |
| Signal Protocol | ISL32179 or TTL |
These compact devices are designed to fit into tight spaces while delivering reliable performance across various applications.
How Incremental Rotary Encoders Measure Rotational Movement
Incremental rotary encoders measure rotational movement using advanced methodologies. One common method is optical detection, where a transparent disk with opaque sections interacts with a light source and a photo detector. This setup generates signals based on the disk’s rotation. Another method involves pulse generation, where the encoder produces a series of equally spaced pulses, measured in pulses per revolution (PPR).
To determine direction, incremental encoders use a quadrature output with two channels. The phase relationship between these channels indicates whether the shaft is moving clockwise or counterclockwise. This combination of precision and directional sensing makes incremental rotary encoders indispensable in automation.
| Methodology | Description |
|---|---|
| Optical Detection | Uses a transparent disk and light sensors to detect position and velocity. |
| Pulse Generation | Produces pulses corresponding to the shaft’s rotation. |
| Direction Sensing | Determines direction using phase differences between two output channels. |
Key Components and Signal Output
The core components of an incremental rotary encoder include a rotating disk, a light source (or magnetic sensor), and a detector. The disk contains a pattern of slots or opaque regions that interact with the light source to produce signals. These signals are then processed to provide feedback on the shaft’s position and movement.
Incremental rotary encoders typically offer versatile signal outputs, such as A phase, B phase, and Z phase. These outputs can be configured for different applications, ensuring seamless integration into your automation system. Advanced technologies like LowHarmonics ensure high-quality SinCos signals, while interference-proof sensing enhances reliability in challenging environments.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| LowHarmonics technology | Ensures excellent SinCos signal quality. |
| Interference-proof sensing | Provides precise sensing with electromagnetic compatibility. |
| Signal transmission reliability | Supports long-distance signal transmission, up to 550 m for TTL signals. |
By combining robust components with reliable signal output, incremental rotary encoders deliver the precision and durability you need for demanding applications.
Key Features of Incremental Rotary Encoders
High Resolution for Accurate Feedback
High resolution is one of the defining features of incremental rotary encoders. These devices measure positions with exceptional precision, thanks to their ability to generate thousands of pulses per revolution. For example, a 12-bit encoder can deliver a resolution of 4,096 points, enabling you to achieve accurate measurements in demanding applications. Whether you need to monitor a leadscrew with increments as small as 0.001 inches or control machinery with intricate movements, the resolution of incremental encoders ensures reliable feedback.
Industry surveys confirm that selecting an encoder with a resolution two to four times better than the maximum error source significantly improves accuracy. This makes incremental rotary encoders indispensable for applications requiring fine-tuned control, such as robotics, CNC machining, and packaging equipment.
Durability and Resistance to Harsh Environments
Incremental rotary encoders are built to withstand challenging conditions. Their mechanical design ensures robustness, allowing them to operate at speeds up to 30,000 rpm with minimal wear. You can rely on these encoders in environments prone to vibration, dust, or extreme temperatures.
Environmental tests highlight their ability to resist corrosion and electromagnetic interference. For instance, optimized materials and coatings protect the encoders in corrosive settings, while EMC-tested designs ensure burst resistance up to 4 kV. Special options are available for operation in arctic, tropical, or desert conditions, making these encoders suitable for diverse industrial applications.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Design | Operates at high speeds with minimal wear, ideal for harsh environments. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Materials and coatings designed for long-term durability in corrosive conditions. |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility | Interference-resistant design tested for burst resistance up to 4 kV. |
| Environmental Suitability | Options for extreme conditions, including arctic and desert environments. |
Versatile Output Options for System Integration
Incremental rotary encoders offer versatile output options, allowing seamless integration into your automation systems. You can choose from open-collector, complementary, or push-pull outputs based on your specific requirements. These outputs support various protocols, including parallel binary, analog voltage, and network protocols like Profinet and EtherNet/IP.
Line drivers enhance performance by ensuring low-impedance output and excellent noise immunity. They support cable lengths up to 1,000 feet and frequencies up to 1 MHz, making them ideal for long-distance signal transmission. Open collectors, while bandwidth-limited, are suitable for shorter distances and lower frequencies.
- Key Benefits of Output Options:
- Directional information enhances resolution up to four times with compatible devices.
- Reliable signal transmission ensures consistent feedback in complex systems.
- Flexible configurations adapt to diverse industrial needs.
These features make incremental rotary encoders a versatile and reliable choice for automation systems, ensuring precision and efficiency across various applications.
Applications of Incremental Rotary Encoders in Automation
Speed Monitoring and Control in Machinery
Incremental rotary encoders play a critical role in monitoring and controlling the speed of machinery. These devices generate pulses that correspond to the rotational movement of a shaft, allowing you to measure speed with precision. By analyzing the frequency of these pulses, you can ensure that machinery operates at optimal speeds, improving efficiency and reducing wear.
Technological advancements have enhanced the performance of these encoders, making them more accurate and durable. The integration of IoT and AI technologies further boosts their capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This ensures that your machinery remains reliable and efficient, even in demanding industrial environments.
| Key Takeaways | Description |
|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Continuous improvements in resolution, accuracy, and durability. |
| Growing Automation | Increased demand for precise position sensing in smart manufacturing. |
| Diverse Applications | Used in robotics, automotive, and consumer electronics. |
Position Feedback in Robotics and Packaging Equipment
In robotics and packaging equipment, precise position feedback is essential for smooth operation. Incremental rotary encoders provide this feedback by outputting a defined number of pulses per revolution. This allows you to measure angles and distances accurately, ensuring that robotic arms and packaging machines perform their tasks with precision.
These encoders are widely used in applications requiring high-precision positioning, such as inspection systems and conveyor belts. Their ability to deliver real-time feedback makes them indispensable in automation settings where accuracy is paramount.
- Applications include:
- Food processing lines.
- Automotive assembly systems.
- High-precision inspection equipment.
Precision Control in Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes demand precision to maintain quality and efficiency. Incremental rotary encoders help you achieve this by providing accurate measurements of rotational movement. Higher pulse outputs lead to better resolution, enabling you to control machinery with greater accuracy.
These encoders are particularly useful in CNC machining, where even the smallest error can impact the final product. By delivering reliable feedback, they ensure that your manufacturing processes remain consistent and efficient. The growing demand for automation and precision control continues to drive the adoption of these encoders across various industries.
Incremental Rotary Encoders vs. Absolute Encoders
Differences in Functionality and Output
Incremental rotary encoders and absolute encoders serve similar purposes but differ in how they operate and deliver output. Incremental rotary encoders generate pulses as the shaft rotates. These pulses provide relative position, speed, and direction information. However, they do not retain position data when powered off.
Absolute encoders, on the other hand, assign a unique digital code to each position. This allows them to remember the exact position even after a power loss. While incremental encoders are ideal for applications requiring speed and direction tracking, absolute encoders excel in scenarios where position memory is critical.
| Feature | Incremental Rotary Encoder | Absolute Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Position Memory | No | Yes |
| Output | Pulses | Unique Digital Code |
| Common Applications | Speed and Direction Tracking | Position Monitoring |
Advantages of Incremental Encoders in Compact Applications
Incremental rotary encoders offer significant benefits in compact applications. Their small size and lightweight design make them perfect for machinery with limited space. For example, the GOS25C Series encoder has an outer diameter of just 25mm, making it ideal for tight spaces.
These encoders also provide high resolution, ensuring precise feedback in compact systems. With resolutions up to 4,096 pulses per revolution, they deliver the accuracy needed for tasks like robotic arm movement or conveyor belt control. Their durability and resistance to harsh environments further enhance their suitability for compact, high-performance applications.
Choosing the Right Encoder for Your Needs
Selecting the right encoder depends on your application requirements. If you need precise speed and direction tracking, an incremental rotary encoder is the best choice. Its high resolution and compact design make it ideal for machinery requiring precision in small spaces.
For applications where position memory is essential, such as in power-off scenarios, an absolute encoder is more suitable. Consider factors like resolution, environmental conditions, and output type when making your decision. Consulting with an expert can help you choose the encoder that best fits your needs.
Incremental rotary encoders, like the GOS25C Series, provide the precision you need for automation systems. Their high resolution ensures accurate feedback, while the compact design fits seamlessly into tight spaces. You can rely on their durability to perform in harsh environments, making them ideal for demanding applications. Whether you’re optimizing machinery or enhancing manufacturing processes, these encoders deliver reliable and accurate results. Consider using an incremental rotary encoder to achieve greater efficiency and precision in your automation projects.
FAQ
What is the difference between incremental and absolute rotary encoders?
Incremental encoders provide relative position data through pulses, while absolute encoders assign a unique digital code to each position. Incremental encoders excel in speed and direction tracking, whereas absolute encoders retain position data even after power loss.
How do you choose the right resolution for an incremental rotary encoder?
Select a resolution based on your application’s precision needs. Higher resolutions, like 4,096 pulses per revolution, offer finer control. For general tasks, lower resolutions may suffice. Always match the resolution to the accuracy required by your system.
Tip: Consult your system’s specifications to avoid over- or under-specifying the encoder.
Can incremental rotary encoders work in harsh environments?
Yes, many incremental encoders, like the GOS25C Series, are designed for durability. They resist dust, vibration, and extreme temperatures. This makes them reliable in challenging industrial settings.
What are the common output options for incremental rotary encoders?
Incremental encoders offer outputs like open-collector, complementary, and push-pull. These options support various protocols, ensuring compatibility with different systems. Choose the output type that matches your system’s requirements for seamless integration.
Why are incremental rotary encoders important in automation?
They provide precise feedback on position, speed, and direction. This ensures accurate control of machinery, improving efficiency and reducing errors. Their compact design and high resolution make them essential for modern automation systems.
Note: Incremental encoders are a cost-effective solution for applications requiring precision without position memory.